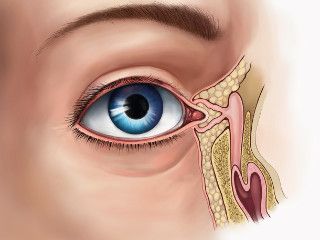
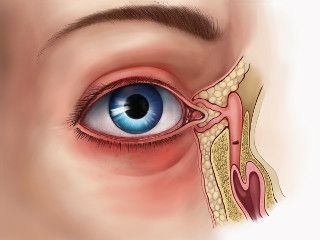
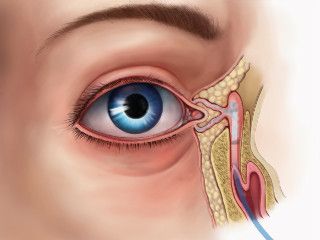
Surgery of dacryocystitis of lacrimal obstruction. Probing the nasolacrimal canals
Probing in the case of dacryocystitis
When probing, the surgeon inserts a special probe into the nasolacrimal canal directly through the lacrimal point. It is extremely important to perform this manipulation very accurately, so that not to harm the baby. But the awake child will actively resist. And in this case, when probing, there is a high probability of creating a false opening in the nasolacrimal canal or fistulas, which inevitably leads to the development of complications and the need for repeated probing.
Stenting of the lacrimal canal
Stenting is conducted in cases of improper development of the canaliculi.
To do this, we install a special stent. In complex cases, it is required to form a new fistula, which ensures the outflow of tears into the nasal cavity with subsequent stenting. These operations are performed together with the otolaryngologist under the process video control of manipulation.
Before conducting probing and stenting, children are necessarily examined by narrow-focused specialists, a cardiologist, a pediatrician, and an otolaryngologist, to exclude contraindications to anesthesia. Their conclusions are necessary for the anesthetist who selects the ideal method for providing a drug-induced sleep and who is responsible for the overall condition of the child during this procedure.
When to treat dacryocystitis?
Dacryocystitis occurs in 10-15% of newborns.
The most ideal age for conducting probing in a drug-induced sleep is 2-6 months. But do not wait for the child to reach 6 months of age specifically. With prolonged inflammation, the walls of the tear sac become flabby, and it may lose its function of the pump that pumps the tear.