Visual evoked potentials (VEPs are performed to assess the functional state of the visual system and identify subtle specific abnormalities.
This examination method is electrophysiological and it is indispensable for identifying meridian amblyopia, optic nerve atrophy, for assessing the results of treatment, and for dynamic follow-up of the state of the visual system in the case of strabismus, nystagmus, amblyopia, and optic nerve atrophy.
We perform VEPs for children over 3 months of age.
In children under 2 years of age, VEPs are used as an examination that helps monitor the maturation of the optic pathway, thus, the examination may be conducted once every 3 months and 1 time a year on average after the age of 2.
The examination lasts 30 minutes to 1 hour.
Method of preparation of a child for the VEPs examination:
- The night before, wash your child's head without using balms.
- The child should get a good night's sleep.
- If your child wears glasses, be sure to bring them with you. If the child wears contact lenses, it is also recommended to take them with you or come wearing them (some types of examinations are better to conduct in contact correction). Don't forget to take a container with the solution for the case you need to take off the lenses.
- If your daughter wears earrings, take off them in advance.
- If you take any medications regularly, take them as normal. Other medications that you periodically take is better not to use before the examination. Tell your doctor who is going to conduct the examination of all the medications you use.
- Arrive in advance and try to make the child relax before the examination.
Recommendations depend on the type of electrophysiological examination and may vary.
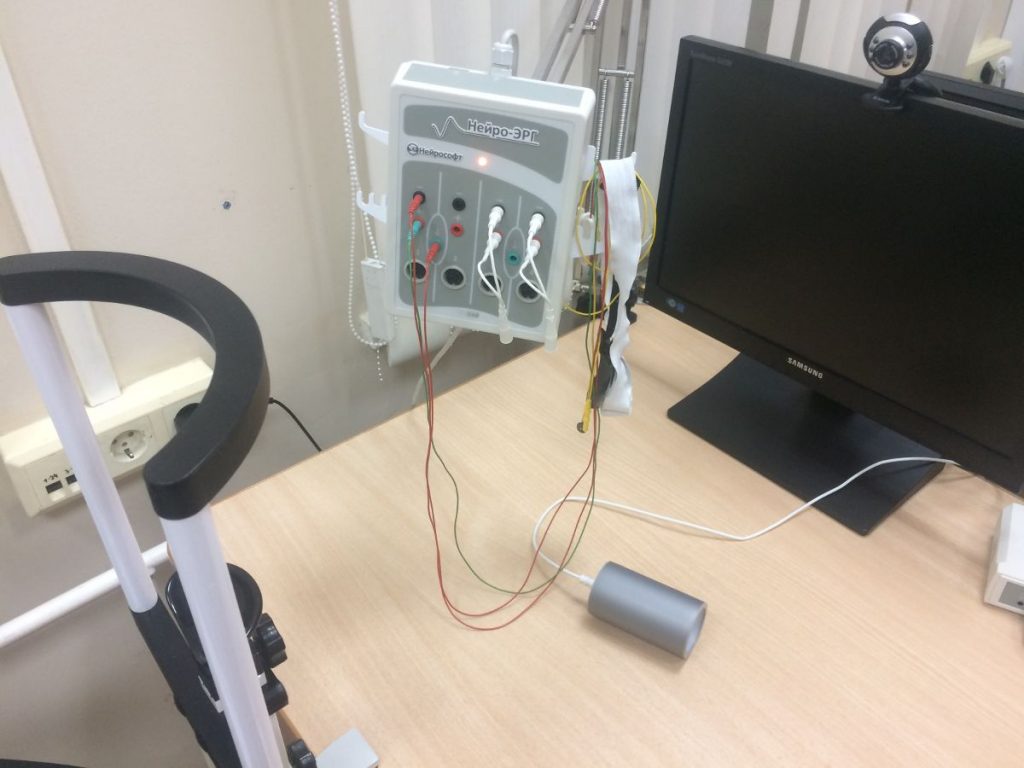
VEPs procedure
VEPs is a safe and non-invasive procedure. Prepare your child for VEPs:
-
Before starting the examination, the doctor will apply several electrodes to the earlobes and to the head. A saline solution, a contact gel, or a paste is sometimes used for this purpose.
- The doctor will give you or your child instructions on behavior during the examination. Usually, each eye is examined separately (the other eye is closed with an occluder or flap).
- After the procedure, the electrodes and contact gel are removed.
Following the examination, the doctor will analyze the results and discuss the conclusion with you.